Approximation of Pi (π)
- XR_XharpRazor
- Aug 25, 2021
- 1 min read
Updated: Jan 20
M2007U-E2016-A2017-S2017-M2021_SMT-20160929x01
Let's draw a circle with a radius of r, and install a polygon inside it.
As the number of the sides of the polygon increases,
the polygon is approaching a circle, but the polygon will never be a circle.
cutting the polygon into several equal triangles with one of their tips at the center of the circle,
let's call the angle between 2 radii as θ.
as the side of the polygon increases, the angle θ becomes smaller and smaller,
the number of sides also indicates the number of triangles having one of its vertices as the center of the circle we have.
Therefore
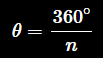
where n is the number of sides we have / the number of triangles we have
since we know that the area of a triangle is

in this case, a = b = r, so
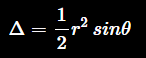
since a single triangle has an area like that, then the whole polygon should have n times of that area, so we will have

as n increases, the polygon will approximately become a circle, and therefore the area would be

we can also write the equation with a variable approaching 0 instead of infinity by setting
n = 1/x, when n→∞, then x→0+
therefore


.png)















Comments